Hadoop
Hadoop is an Apache-managed software framework derived from MapReduce and Big Table. Hadoop allows applications based on MapReduce to run on large clusters of commodity hardware. Hadoop is designed to parallelize data processing across computing nodes to speed computations and hide latency. Two major components of Hadoop exist: a massively scalable distributed file system that can support petabytes of data and a massively scalable MapReduce engine that computes results in batch.
Hadoop is an essential tool for managing big data. This tool fills a rising need for businesses managing large data stores, or data lakes as Hadoop refers to them. The biggest need in business, when it comes to data, is the ability to scale. Technology and business are driving organizations to gather more and more data, which increases the need to manage it efficiently.
In building the Hadoop Stack, each component plays an important role in the platform. The stack starts with the essential requirements contained in the Hadoop Common, which is a collection of common utilities and libraries that support other Hadoop modules. Like any stack, these supportive files are a necessary requirement for a successful implementation. The well-known file system, the Hadoop Distributed File System or HDFS, is at the heart of Hadoop. To narrow your perspective on a set of data, you can use the programming logic contained within MapReduce, which provides massive scalability across many servers in a Hadoop cluster. For resource management, you can consider adding Hadoop YARN, the distributed operating system for your big data apps, to your stack.
The Components of Hadoop
The Hadoop Common is the foundation of Hadoop, because it contains the primary services and basic processes, such as the abstraction of the underlying operating system and its filesystem. Hadoop Common also contains the necessary Java Archive (JAR) files and scripts required to start Hadoop. The Hadoop Common package even provides source code and documentation, as well as a contribution section. You can’t run Hadoop without Hadoop Common.
The Distributed File System (HDFS)
HDFS delivers a distributed filesystem that is designed to run on basic hardware components. Most businesses find these minimal system requirements appealing. This environment can be set up in a Virtual Machine (VM) or a laptop for the initial walkthrough and advancement to server deployment. It is highly fault-tolerant and is designed to be deployed on low-cost hardware. It provides high throughput access to application data and is suitable for applications having large datasets.
Hardware failures are unavoidable in any environment. With HDFS, your data can span across thousands of servers, with each server containing an essential piece of data. This is where the fault tolerance feature comes into play. The reality is that with this many servers there is always the risk that one or more may become nonfunctional. HDFS has the ability to detect faults and quickly perform an automatic recovery.
What is MapReduce?
MapReduce is a programming component of Hadoop used for processing and reading large data sets. The MapReduce algorithm gives Hadoop the ability to process data in parallel. In short, MapReduce is used to compress large amounts of data into meaningful results for statistical analysis. MapReduce can do batch job processing, which is the ability to read large amounts of data numerous times during processing to produce the requested results.
For businesses and organizations with large data stores or data lakes, this is an essential component in getting your data down to a manageable size to analyze or query.
The MapReduce workflow, as shown in the below figure, works like a grandfather clock with a number of gears. Each gear performs a particular task before it moves on to the next. It shows the transitional states of data as it is chunked into smaller sizes for processing.
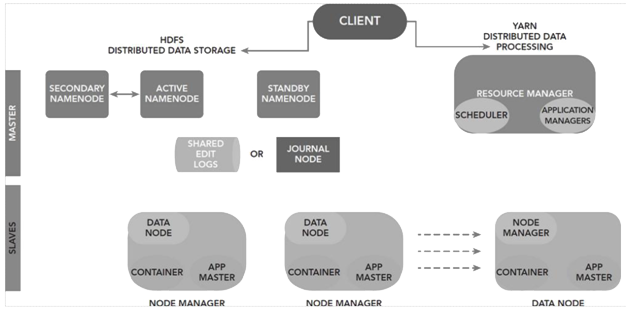
What is YARN?
The YARN Infrastructure (Yet Another Resource Negotiator) is the framework responsible for providing the computational resources (memory, CPUs, etc.) needed for executing applications.
Two important components of YARN are Resource Manager and Node Manager. Let’s build the profile of YARN. First consider a two level cluster where Resource Manager is in the top tier (one per cluster). The Resource Manager is the master. It knows where the slaves are located (lower tier) and how many resources they have. It runs several services, and the most important is the Resource Scheduler, which decides how to assign the resources. The Node Manager (many per cluster) is the slave of the infrastructure. When it starts, it announces itself to the Resource Manager. The node has the ability to distribute resources to the cluster, and its resource capacity is the amount of memory and other resources. At run-time, the Resource Scheduler will decide how to use this capacity. The YARN framework in Hadoop allows workloads to share cluster resources dynamically between a variety of processing frameworks, including MapReduce, Impala, and Spark. YARN currently handles memory and CPU and will coordinate additional resources like disk and network I/O in the future.
What is ZOOKEEPER?
ZooKeeper is another Hadoop service—a keeper of information in a distributed system environment. ZooKeeper’s centralized management solution is used to maintain the configuration of a distributed system. Because ZooKeeper is maintaining the information, any new nodes joining will acquire the up-to-date centralized configuration from ZooKeeper as soon as they join the system. This also allows you to centrally change the state of your distributed system just by changing the centralized configuration through one of the ZooKeeper clients.
The Name service is a service that maps a name to some information associated with that name. It is similar to Active Directory being a name service that maps the user id (name) of a person to certain access or rights within an environment. In the same way, a DNS service is a name service that maps a domain name to an IP address. By using ZooKeeper in a distributed system you can keep track of which servers or services are up and running and look up their status by name.
If there is a problem with nodes going down, ZooKeeper has an automatic fail-over strategy via leader election as an off-the-shelf support solution. Leader election is a service that can be installed on several machines for redundancy, but only one is active at any given moment. If the active service goes down for some reason, another service rises to do its work.
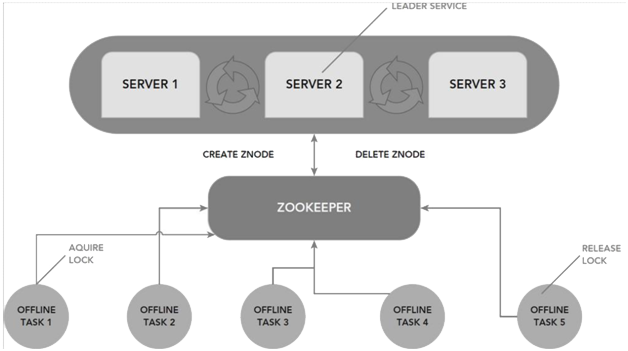
ZooKeeper allows you to process more data, more reliably and in less time. ZooKeeper can help you build more robust systems. A managed database cluster can benefit from centralized management services in terms of name services, group services, leader election, configuration management, and more. All of these coordination services can be managed with ZooKeeper.
What is HIVE?
Hive was originally designed to be a part of Hadoop, but now it is a standalone component. It is a data warehouse infrastructure built on top of Hadoop for providing data summarization, query, and analysis.
If you are longing for the database experience and missing the structure of a relational environment when working with Hadoop, this might be your solution. Keep in mind this is not to be compared to a traditional database or data structure. Nor can it replace your existing RDBMS environment. Hive provides a conduit to project structure onto this data, and queries the data using a SQL-like language called HiveQL.
